Nucleic acids, macromolecules made out of units called nucleotides, come in two naturally occurring varieties: deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) and ribonucleic acid ( RNA ). DNA is the genetic material found in living organisms, all the way from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals like you and me. Some viruses use RNA, not DNA, as their
Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry – Biomolecules – CBSE Tuts
A carbon-nitrogen bond is a covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen and is one of the most abundant bonds in organic chemistry and biochemistry. [1] Nitrogen has five valence electrons and in simple amines it is trivalent, with the two remaining electrons forming a lone pair.

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
Figure 4. Sucrose is formed when a monomer of glucose and a monomer of fructose are joined in a dehydration reaction to form a glycosidic bond. In the process, a water molecule is lost. By convention, the carbon atoms in a monosaccharide are numbered from the terminal carbon closest to the carbonyl group.

Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
CH105: Chapter 5 – Introduction to Organic Chemistry – Chemistry
Jan 4, 2024biomolecule, any of numerous substances that are produced by cells and living organisms. Biomolecules have a wide range of sizes and structures and perform a vast array of functions. The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Among biomolecules, nucleic acids, namely DNA and RNA, have the unique

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
Which Biomolecule Does Not Have A Carbon-Nitrogen Bond
Jan 4, 2024biomolecule, any of numerous substances that are produced by cells and living organisms. Biomolecules have a wide range of sizes and structures and perform a vast array of functions. The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Among biomolecules, nucleic acids, namely DNA and RNA, have the unique
There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s mass. Biological macromolecules are organic, meaning that they contain carbon (with
Biomolecules | PPT
B. DNA and proteins have the same structure and function together to make carbohydrates. C. DNA and proteins are nucleic acids that function together to maintain oxygen in the respiratory system. D. DNA and proteins are made of polymers that function in controlling substances entering the cell membrane. Answer i chose DNA and proteins are made
SOLVED: ‘Which bio molecule is not found in cell membrane 1. Which biomolecule is not found in cell membranes? Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids 2. What are the building blocks of a
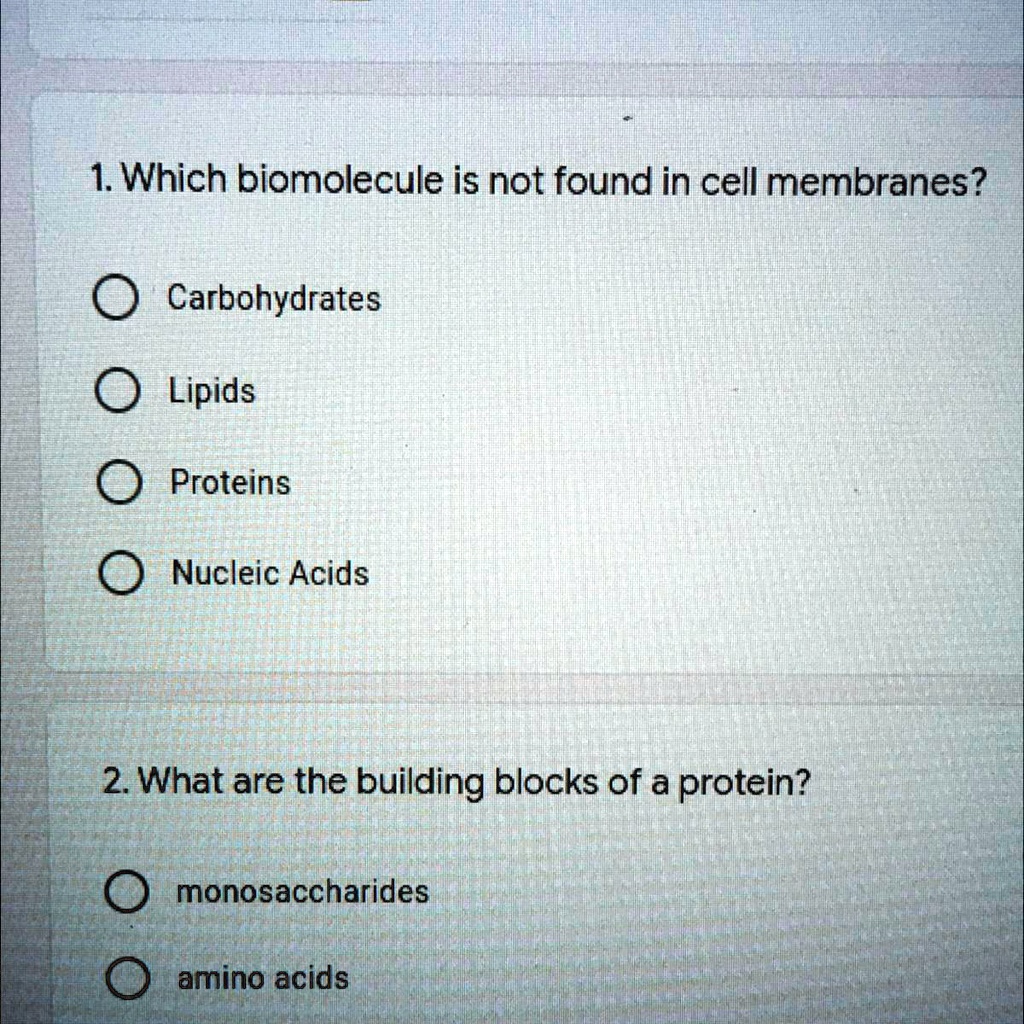
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Biological Molecules | Biology I
B. DNA and proteins have the same structure and function together to make carbohydrates. C. DNA and proteins are nucleic acids that function together to maintain oxygen in the respiratory system. D. DNA and proteins are made of polymers that function in controlling substances entering the cell membrane. Answer i chose DNA and proteins are made

Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry – Biomolecules – CBSE Tuts
Nucleic acids, macromolecules made out of units called nucleotides, come in two naturally occurring varieties: deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) and ribonucleic acid ( RNA ). DNA is the genetic material found in living organisms, all the way from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals like you and me. Some viruses use RNA, not DNA, as their

Source Image: cbsetuts.com
Download Image
CH105: Chapter 5 – Introduction to Organic Chemistry – Chemistry
Figure 4. Sucrose is formed when a monomer of glucose and a monomer of fructose are joined in a dehydration reaction to form a glycosidic bond. In the process, a water molecule is lost. By convention, the carbon atoms in a monosaccharide are numbered from the terminal carbon closest to the carbonyl group.
Source Image: wou.edu
Download Image
Chapter 1: The Foundations of Biochemistry – Chemistry
Which biomolecule does NOT have a carbon-nitrogen bond? O protein O peptide O nucleic acid O carbohydrate Which biomolecule does NOT have a carbon-nitrogen bond? O protein O peptide O nucleic acid O carbohydrate Biology 2e 2nd Edition ISBN: 9781947172517 Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Source Image: wou.edu
Download Image
Biological Molecules Quiz Questions – Trivia & Questions
Jan 4, 2024biomolecule, any of numerous substances that are produced by cells and living organisms. Biomolecules have a wide range of sizes and structures and perform a vast array of functions. The four major types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Among biomolecules, nucleic acids, namely DNA and RNA, have the unique

Source Image: proprofs.com
Download Image
Different Types of Biological Macromolecules | Biology for Majors I
There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids), and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s mass. Biological macromolecules are organic, meaning that they contain carbon (with

Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
Biological Molecules | Biology I
Different Types of Biological Macromolecules | Biology for Majors I
A carbon-nitrogen bond is a covalent bond between carbon and nitrogen and is one of the most abundant bonds in organic chemistry and biochemistry. [1] Nitrogen has five valence electrons and in simple amines it is trivalent, with the two remaining electrons forming a lone pair.
CH105: Chapter 5 – Introduction to Organic Chemistry – Chemistry Biological Molecules Quiz Questions – Trivia & Questions
Which biomolecule does NOT have a carbon-nitrogen bond? O protein O peptide O nucleic acid O carbohydrate Which biomolecule does NOT have a carbon-nitrogen bond? O protein O peptide O nucleic acid O carbohydrate Biology 2e 2nd Edition ISBN: 9781947172517 Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark